Food Packing Industry in Italy: Structure, Processes, and Industry Conditions
The food packing industry in Italy is built around organized packaging processes designed to preserve product quality and consistency. Activities usually follow defined steps within controlled environments. This overview explains how food packaging operates and highlights typical conditions associated with the industry.
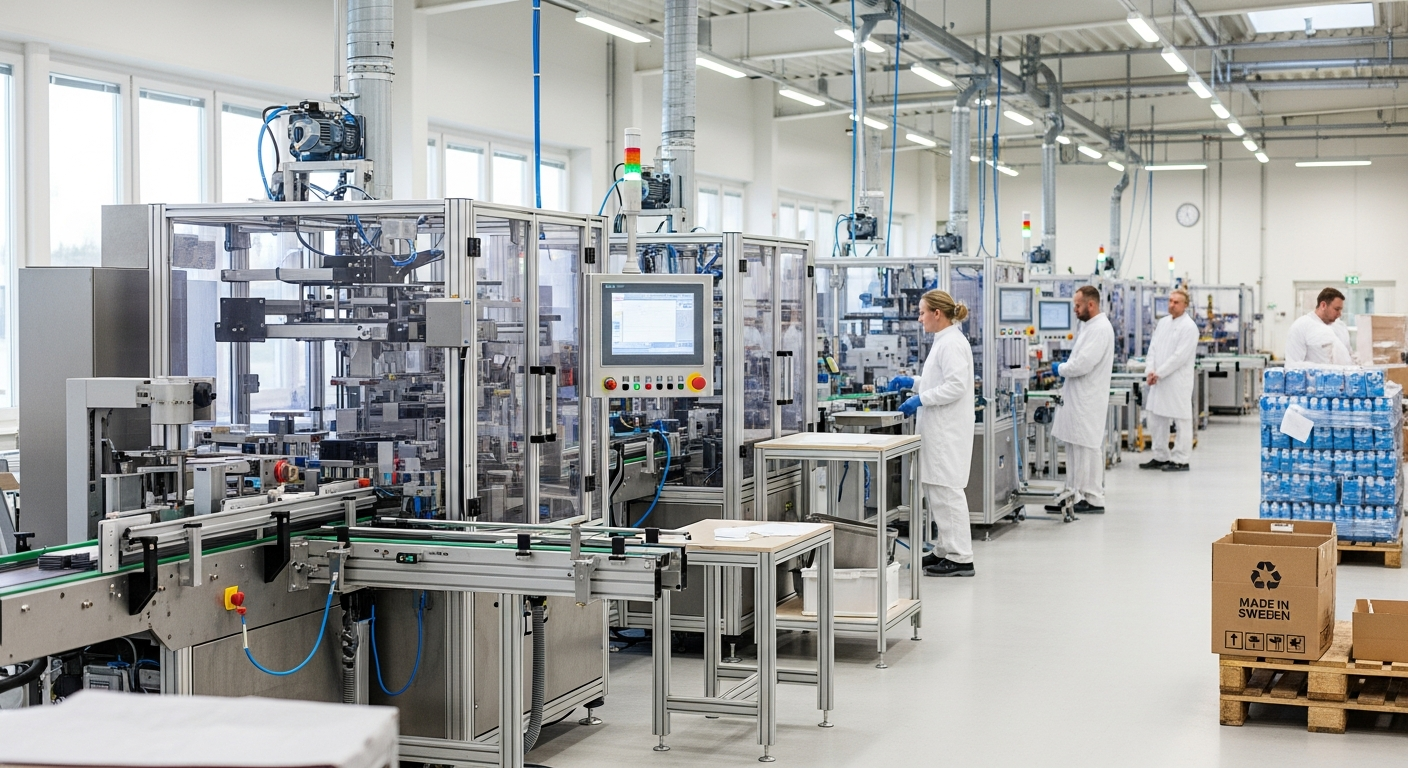

Italy’s food packing sector has evolved into a sophisticated industry that balances heritage food production methods with contemporary packaging technologies. The country’s reputation for quality food products extends to how these items are preserved, protected, and presented to consumers. This industry serves both domestic consumption and significant export markets, requiring adherence to stringent standards while maintaining efficiency and sustainability.
Overview of the Food Packing Sector in Italy
The Italian food packing sector encompasses multiple subsectors, including meat processing, dairy packaging, bakery products, fresh produce handling, and frozen food preparation. Major industrial zones are concentrated in northern regions such as Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Veneto, though facilities operate throughout the peninsula. The industry employs a substantial workforce across various skill levels, from manual packers to quality control specialists and machine operators. Companies range from small family-owned operations specializing in artisanal products to large multinational corporations with automated production lines. The sector contributes significantly to the national economy, with packaging materials and machinery manufacturing forming complementary industries that support food packing operations.
Structure of the Food Packaging Process
Food packaging processes in Italy typically follow systematic workflows designed to maintain product integrity while maximizing efficiency. Initial stages involve receiving raw materials or semi-processed foods, followed by quality inspections to ensure only acceptable products enter the packaging line. Preparation phases may include washing, cutting, portioning, or cooking depending on the product type. Primary packaging involves direct contact with food items, using materials such as plastic films, paper, cardboard, glass, or metal containers. Secondary packaging groups primary packages into larger units for distribution, while tertiary packaging prepares products for transportation. Throughout these stages, hygiene protocols remain paramount, with facilities maintaining controlled environments that prevent contamination. Traceability systems track products from origin through final packaging, enabling rapid response to quality issues.
Food Quality Systems and Standards
Italian food packing operations must comply with comprehensive quality and safety frameworks established by European Union regulations and national authorities. The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points system forms the foundation of food safety management, identifying potential risks at each production stage and implementing preventive measures. Facilities typically hold certifications such as ISO 22000 for food safety management, BRC Global Standards, or IFS Food Standards, demonstrating compliance with international benchmarks. Regular inspections by health authorities verify adherence to hygiene requirements, proper temperature controls, and accurate labeling. Many companies implement additional quality assurance protocols beyond minimum legal requirements, including organoleptic testing, microbiological analysis, and shelf-life studies. Documentation systems record all quality checks, enabling complete traceability and facilitating continuous improvement initiatives.
Organized Workflows and Technological Innovation
Modern Italian food packing facilities increasingly incorporate technological solutions to enhance productivity and consistency. Automated packaging lines reduce manual handling while increasing throughput, with machines capable of forming packages, filling contents, sealing, and labeling at high speeds. Robotics systems handle repetitive tasks such as sorting, palletizing, and quality inspection, reducing physical strain on workers while improving accuracy. Vision systems equipped with cameras and sensors detect defects, verify correct labeling, and ensure proper seal integrity. Many facilities have adopted Industry 4.0 principles, integrating connected devices that collect real-time production data for analysis and optimization. Despite technological advancement, human oversight remains essential for quality judgment, machine maintenance, and handling specialized products that require manual attention. Training programs ensure workers can operate sophisticated equipment while maintaining traditional quality standards.
Current Industry Conditions and Trends
The Italian food packing industry currently navigates several significant trends reshaping operational practices. Sustainability initiatives drive adoption of eco-friendly packaging materials, including biodegradable plastics, recycled content, and reduced material usage through lightweighting strategies. Consumer demand for transparency has intensified focus on clear labeling, origin information, and ethical production practices. E-commerce growth requires packaging designs that withstand direct-to-consumer shipping while maintaining product quality and visual appeal. Labor market dynamics present ongoing challenges, with facilities seeking workers willing to perform repetitive tasks in temperature-controlled environments, often during shift work schedules. Regulatory evolution continues with stricter requirements for food contact materials, allergen management, and waste reduction. Companies investing in automation and worker training demonstrate greater resilience amid these changing conditions, positioning themselves competitively within domestic and international markets.
The food packing industry in Italy reflects the nation’s commitment to quality food production while embracing necessary modernization. Facilities that successfully balance traditional standards with technological innovation, maintain rigorous quality systems, and adapt to evolving market demands contribute to the sector’s continued relevance. Understanding the structured processes, regulatory frameworks, and current trends provides comprehensive insight into this essential component of Italy’s food economy. As consumer preferences and environmental considerations continue shaping industry practices, Italian food packing operations demonstrate ongoing adaptation while preserving the quality expectations associated with Italian food products.